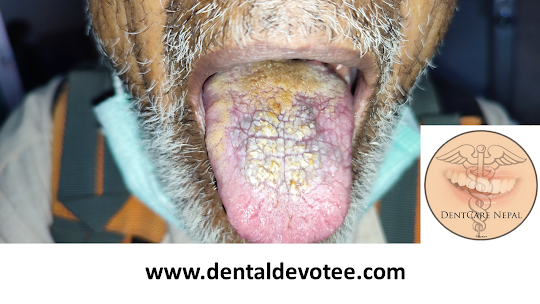
Candidiasis is a disease caused by infection with a yeast like fungus, Candida albicans, although other species may also be involved, such as C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis, C. stellatoidea, C. krusei, C. glabrata, C. pseutropicalis and C. guilliermondii. Candidiasis is the most common opportunistic infection in the world. Its occurrence has surged since the prevalent use of antibiotics, which destroy the normal inhibitory bacterial flora, and immunosuppressive drugs, particularly corticosteroids and cytotoxic drugs. Oral candidiasis or oral thrush usually remain as a localized disease, but on occasion it may show extension to the pharynx or even to the lungs.
Some specific conditions that may predispose a patient to develop oral candidiasis are:
❍ Factors that alter the immune status of the host
❍ Diabetes mellitus
❍ Corticosteroid therapy/hypoadrenalism
❍ Blood dyscrasias or advanced malignancy
❍ Old age/infancy
❍ Radiation therapy/chemotherapy
❍ HIV infection or other immunodeficiency disorders
❍ Endocrine abnormalities
❍ Hypothyroidism or hypoparathyroidism
❍ Pregnancy
Clinical presentation
Acute pseudomembranous candidiasis: Pseudomembranous candidiasis is the most common form of oral candidiasis. The most common sites of occurrence include buccal mucosa, dorsal tongue and palate. It is usually seen after antibiotic therapy or immunosuppression. A burning sensation usually
precedes the appearance of soft, creamy white to yellow, elevated plaques, that are easily wiped off from the affected oral tissues and leave an erythematous, eroded, or ulcerated surface which may be tender. Candidiasis may be seen in neonates and among terminally ill patients, particularly in association with serious underlying conditions such as leukemia and other malignancies and in HIV
disease.
Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis: (candida leukoplakia) Hyperplastic candidiasis is seen as chronic, discrete raised lesions that vary from small, palpable translucent whitish areas to large, dense, opaque plaques, hard and rough to touch. The most common sites are the anterior buccal mucosa along the occlusal line, and laterodorsal surfaces of the tongue. The most common appearance is that of asymptomatic white plaques or papules (sometimes against an erythematous background) that are adherent and do not scrape off.
Chronic atrophic (erythematous) candidiasis: The most common site is the hard palate under a denture
but atrophic candidiasis may also be found on the dorsal tongue and other mucosal surfaces. The most common etiology is poor denture hygiene, and/or continuous denture insertion, but it may also be caused by immunosuppression, xerostomia, or antibiotic therapy.
Median rhomboid glossitis: Median rhomboid glossitis is a form of chronic atrophic candidiasis characterized by an asymptomatic, elongated, erythematous patch of atrophic mucosa of the posterior mid-dorsal surface of the tongue due to a chronic Candida infection. In the past, median rhomboid glossitis was thought to be a developmental defect resulting from a failure of the tuberculum impart to retract before fusion of the lateral processes of the tongue.
Angular cheilitis (perleche): Clinical appearance is that of red, eroded, fissured lesions which occur bilaterally in the commissures of the lips and are frequently irritating and painful. The most common etiology is loss of vertical occlusal dimension, but it may also be associated with immunosuppression.
Chronic multifocal oral candidiasis: This term has been given to chronic candidal infection that may be seen in multiple oral sites, with various combinations, including angular stomatitis, median rhomboid glossitis and palatal lesions.
Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis (CMC): It is the term given to the group of rare syndromes, with definable immune defects, in which there is persistent mucocutaneous candidiasis that responds poorly to topical antifungal therapy.
Treatment:
Topical versus systemic drugs Topical antifungals are usually the drug of choice for uncomplicated, localized candidiasis in patients with normal immune function. Systemic antifungals are usually indicated in cases of disseminated disease and/or in immunocompromised patients.
Topical antifungal medications: Nystatin is the first specific antifungal agent effective in the treatment of candidiasis.
Nystatin oral suspension 100,000 units/ml; 300 ml: rinse with one teaspoonful (5 ml) for 2 minutes, use q.i.d. (after meals, and at bedtime) and spit out. Patient can be directed to rinse and swallow if there is
pharyngeal involvement.
Amphotericin B - a cornerstone of therapy for systemic fungal infections.
Clotrimazole - most potent topical agent in azole group of antifungals. 10 mg 70 troches; one troche dissolved in mouth five times per day for 14 days.
Systemic antifungal medications
Ketoconazole tablets, 200 mg 1 tab q.i.d. with a meal or orange juice for 14 days. Ketoconazole is the drug being used in the treatment of chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis and candidiasis
in immunocompromised patients.
Fluconazole tablets, 100 mg, 15 tablets; 2 tablets to start, then 1 tablet q.i.d. for 14 days, oral absorption of fluconazole is rapid and nearly complete within 2 hours.
Itraconazole tablets, 100 mg, 1 tablet b.i.d. with a meal or orange juice for 14 days. This drug has a long half-life and fewer side effects than ketoconazole but is expensive. Its use is contraindicated in liver diseases.
Treatment for chronic atropic candidiasis Application of a thin coat of medicines like nystatin ointment or clotrimazole cream 1% or miconazole cream 2%, ketoconazole cream 2% to entire inner surface of denture after each meal for 14 days usually results in remission. Patient should be instructed to leave dentures out at night and to soak denture in a 1% sodium hypochlorite solution for 15 minutes with thorough rinsing under running water for at least 2 minutes, before bedtime.
Nystatin–triamcinolone acetonide ointment or clotrimazole cream 1% or miconazole cream 2% or ketoconazole cream 2% can be applied to affected areas q.i.d. (after meals, and at bedtime) for 14 days.